How Mars rovers have developed in 25 years of exploring the Pink Planet
Few issues are more durable than hurling a robotic into house — and sticking the touchdown. On the morning of July 4, 1997, mission controllers on the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., have been hoping to beat the chances and land a spacecraft efficiently on the Pink Planet.
Twenty-five years in the past that little robotic, a six-wheeled rover named Sojourner, made it — changing into the primary in a string of rovers constructed and operated by NASA to discover Mars. 4 extra NASA rovers, every extra succesful and sophisticated than the final, have surveyed the Pink Planet. The one named Curiosity marked its tenth yr of cruising round on August 5. One other, named Perseverance, is busy gathering rocks that future robots are presupposed to retrieve and produce again to Earth. China lately bought into the Mars exploring sport, touchdown its personal rover, Zhurong, final yr.
Different Mars spacecraft have performed superb science from a standstill, reminiscent of the dual Viking landers within the Seventies that have been the primary to {photograph} the Martian floor up shut and the InSight probe that has been listening for Marsquakes shaking the planet’s innards (SN On-line: 2/24/20). However the potential to rove turns a robotic into an interplanetary subject geologist, in a position to discover the panorama and piece collectively clues to its historical past. Mobility, says Kirsten Siebach, a planetary scientist at Rice College in Houston, “makes it a journey of discovery.”
Every of the Mars rovers has gone to a special place on the planet, enabling scientists to construct a broad understanding of how Mars developed over time. The rovers revealed that Mars contained water, and different life-friendly circumstances, for a lot of its historical past. That work set the stage for Perseverance’s ongoing hunt for indicators of historical life on Mars.
Every rover can be a mirrored image of the people who designed and constructed and drove it. Perseverance carries on one among its wheels an emblem of Mars rover tracks twisted into the double helix form of DNA. That’s “to remind us, no matter this rover is, it’s of human origin,” says Jennifer Trosper, an engineer on the Jet Propulsion Lab, or JPL, who has labored on all 5 NASA rovers. “It’s us on Mars, and form of our creation.”
The little microwave that might
Sojourner, that first rover, was born in an period when engineers weren’t positive in the event that they even may get a robotic to work on Mars. Within the early Nineties, then-NASA Administrator Daniel Goldin was pushing the company to do issues “sooner, higher and cheaper” — a catchphrase that engineers would mock by saying solely two of these three issues have been attainable on the identical time. NASA had no expertise with interplanetary rovers. Solely the Soviet Union had operated rovers — on the moon in 1970 and 1973.
JPL started growing a Mars rover anyway. Named after the abolitionist Sojourner Reality, the essential machine was the scale of a microwave oven. Engineers have been restricted in the place they may ship it; they wanted a big flat area on Mars as a result of dealing with a precision touchdown close to mountains or canyons was past their talents. NASA selected Ares Vallis, a broad outflow channel from an historical flood, and the mission landed there efficiently.
Sojourner spent almost three months poking across the panorama. It was gradual going. Mission controllers needed to talk with Sojourner continually, telling it the place to roll after which assessing whether or not it had gotten there safely. They made errors: One time they uploaded a sequence of pc instructions that mistakenly advised the rover to close itself down. They recovered from that stumble and plenty of others, studying to shortly repair issues and transfer ahead.
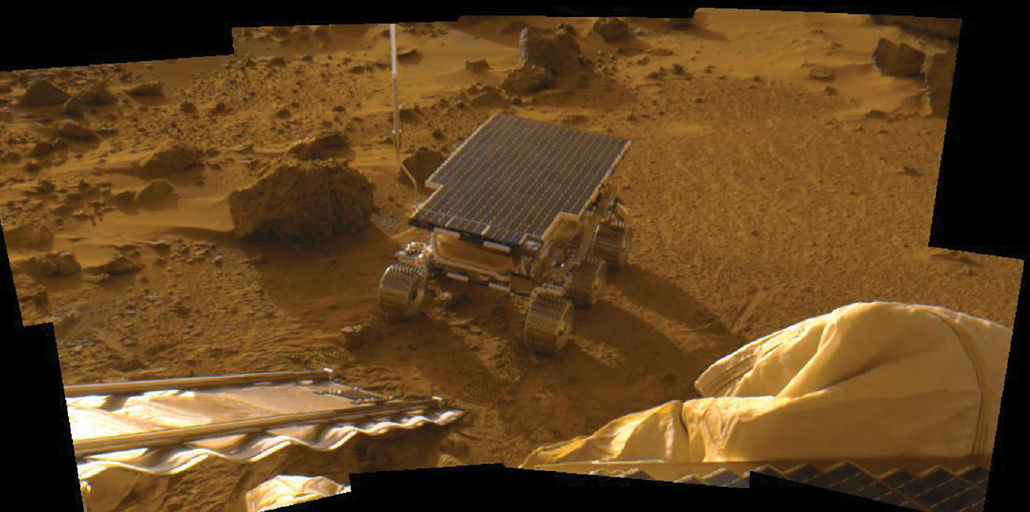

Though Sojourner was a check mission to point out {that a} rover may work, it managed to do some science with its one X-ray spectrometer. The little machine analyzed the chemical make-up of 15 Martian rocks and examined the friction of the Martian soil.
After surviving 11 weeks past its deliberate one-week lifetime, Sojourner in the end grew too chilly to function. Trosper was in mission management when the rover died on September 27, 1997. “You construct this stuff, and even when they’re effectively past their lifetime, you simply can’t let go very simply, as a result of they’re a part of you,” she says.
Twin explorers
In 1998 and 1999, NASA hurled a pair of spacecraft at Mars; one was presupposed to orbit the planet and one other was presupposed to land close to one of many poles. Each failed. Stung from the frustration, NASA determined to construct a rover plus a backup for its subsequent try.
Thus have been born the twins Spirit and Alternative. Every the scale of a golf cart, they have been a significant step up from Sojourner. Every had a robotic arm, a vital improvement in rover evolution that enabled the machines to do more and more subtle science. The 2 had beefed-up cameras, three spectrometers and a software that might grind into rocks to disclose the feel beneath the floor.
However there have been a number of bugs to work out. Spirit and Alternative launched a number of weeks aside in 2003. Spirit bought to Mars first, and on its 18th Martian day on the floor it froze up and began sending error messages. It took mission controllers days to type out the issue — an overloaded flash-memory system — all whereas Alternative was barreling towards Mars. In the end, engineers mounted the issue, and Alternative landed safely on the other facet of the planet from Spirit.
Each rovers lasted years past their anticipated three-month lifetimes. And each did way more Martian science than anticipated.
Spirit broke one among its wheels early on and needed to drive backward, dragging the damaged wheel behind it. However the rover discovered loads to do close to its touchdown web site of Gusev crater, residence to a traditional Mars panorama of mud, rock and hills. Spirit discovered rocks that appeared to have been altered by water way back and later noticed a pair of iron-rich meteorites. The rover in the end perished in 2010, caught in a sand-filled pit. Mission controllers tried to extract it in an effort dubbed “Free Spirit,” however salts had precipitated across the sand grains, making them notably slippery.
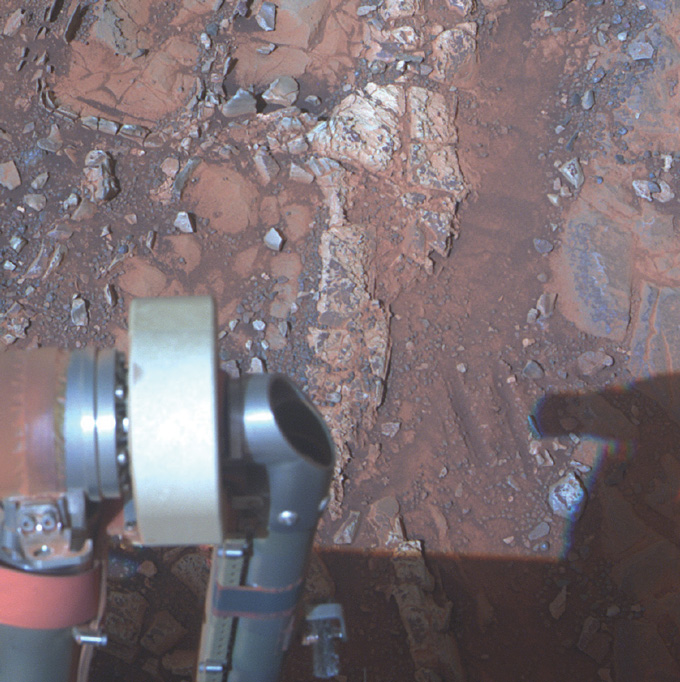
Alternative, in distinction, grew to become the Energizer Bunny of rovers, exploring continually and refusing to die. Instantly after touchdown in Meridiani Planum, Alternative had scientists abuzz.

JPL-CALTECH/NASA, CORNELL UNIV., ARIZONA STATE UNIV.
“The photographs that the rover first despatched again have been simply so completely different from another photographs we’d seen of the Martian floor,” says Abigail Fraeman, a planetary scientist at JPL. “As an alternative of those actually dusty volcanic plains, there was simply this darkish sand and this actually vibrant bedrock. And that was simply so fascinating and galvanizing.”
Proper at its touchdown web site, Alternative noticed the primary definitive proof of previous liquid water on Mars, a much-anticipated and large discovery (SN: 3/27/04, p. 195). The rover went on to seek out proof of liquid water at completely different occasions within the Martian previous. After years of driving, the rover reached a crater known as Endeavour and “stepped into a very new world,” Fraeman says. The rocks at Endeavour have been a whole bunch of tens of millions of years older than others studied on Mars. They contained proof of several types of historical water chemistry.
Alternative in the end drove farther than any rover on any extraterrestrial world, breaking a Soviet rover’s lunar report. In 2015, Alternative handed 26.2 miles (42.2 km) on its odometer; mission controllers celebrated by placing a marathon medal onto a mock-up of the rover and driving it via a end line ribbon at JPL. Alternative lastly died in 2019 after an intense mud storm obscured the solar, reducing off solar energy, vital for the rover to recharge its batteries (SN: 3/16/19, p. 7).
The dual rovers have been an enormous advance over Sojourner. However the subsequent rover was a wholly completely different beast.

The SUV of rovers
By the mid-2000s, NASA had determined it wanted to go massive on Mars, with a megarover the scale of a sports activities utility automobile. The one-ton Curiosity was so heavy that its engineers needed to provide you with a wholly new method to land on Mars. The “sky crane” system used retro-rockets to hover above the Martian floor and slowly decrease the rover to the bottom.
In opposition to all odds, in August 2012, Curiosity landed safely close to Mount Sharp, a 5-kilometer-high pile of sediment throughout the 154-kilometer-wide Gale crater (SN: 8/25/12, p. 5). Not like the primary three Mars rovers, which have been solar-powered, Curiosity runs on vitality produced by the radioactive decay of plutonium. That enables the rover to journey farther and sooner, and to energy a set of subtle science devices, together with two chemical laboratories.
Curiosity launched a brand new method of exploring Mars. When the rover arrives in a brand new space, it seems to be round with its cameras, then zaps attention-grabbing rocks with its laser to determine which of them are value a more in-depth look. As soon as up shut, the rover stretches out its robotic arm and does science, together with drilling into rocks to see what they’re product of.
When Curiosity arrived close to the bottom of Mount Sharp, it instantly noticed rounded pebbles formed by a once-flowing river, the primary shutup have a look at an historical river on Mars. Then mission controllers despatched the rover rolling away from the mountain, towards an space within the crater often known as Yellowknife Bay. There Curiosity found proof of an historical lake that created life-friendly circumstances for doubtlessly many hundreds of years.
Curiosity then headed again towards the foothills of Mount Sharp. Alongside the best way, the rover found a spread of natural molecules in many various rocks, hinting at environments that had been liveable for tens of millions to tens of tens of millions of years. It sniffed methane fuel sporadically wafting inside Gale crater, a still-unexplained thriller that might outcome from geologic reactions, although methane on Earth will be fashioned by dwelling organisms (SN: 7/7/18, p. 8). The rover measured radiation ranges throughout the floor — useful for future astronauts who’ll must gauge their publicity — and noticed mud devils, clouds and eclipses within the Martian environment and night time sky.

MSSS, JPL-Caltech/NASA
“We’ve encountered so many unexpectedly wealthy issues,” says Ashwin Vasavada of JPL, the mission’s undertaking scientist. “I’m simply glad a spot like this existed.”
Ten years into its mission, Curiosity nonetheless trundles on, making new discoveries because it climbs the foothills of Mount Sharp. It lately departed a clay-rich setting and is now getting into one that’s heavier in sulfates, a transition that will replicate a significant shift within the Martian local weather billions of years in the past.
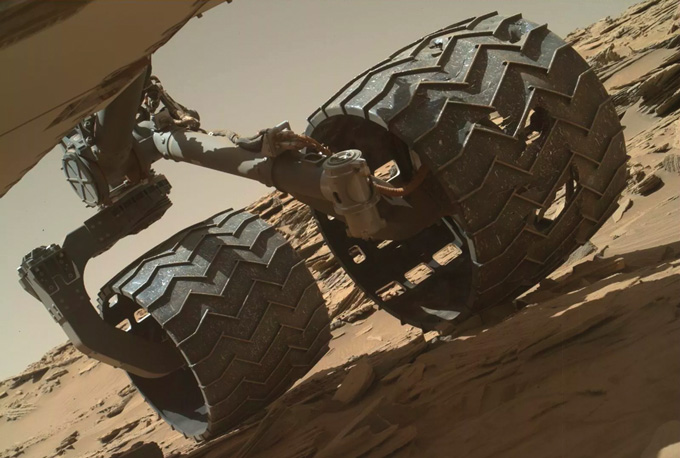
In the middle of driving greater than 28 kilometers, Curiosity has weathered main glitches, together with one which shuttered its drilling system for over a yr. And its wheels have been banged up greater than earthbound assessments had predicted. The rover will proceed to roll till some unknown failure kills it or its plutonium energy wanes, maybe 5 years from now.
MSSS, JPL-Caltech/NASA
A rover and its sidekick
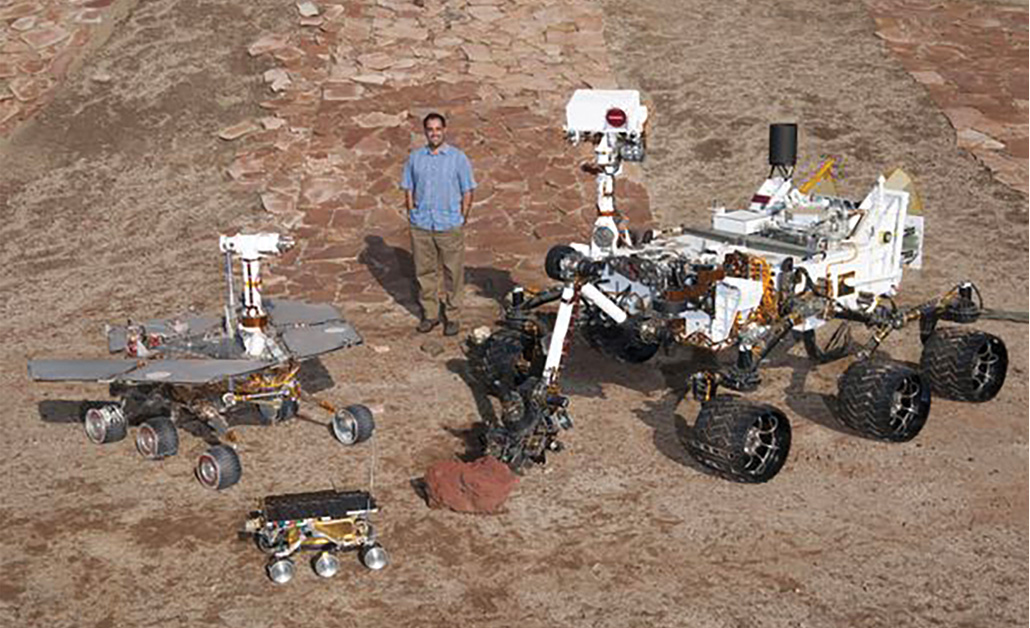
NASA’s first 4 rovers set the stage for probably the most succesful and agile rover ever to go to Mars: Perseverance. Trosper likens the evolution of the machines to the expansion of kids. “We’ve got a preschooler in Sojourner, after which … your happy-go-lucky youngsters in Spirit and Alternative,” she says. “Curiosity is definitely a younger grownup that’s in a position to do a number of issues on her personal, and Perseverance is form of that high-powered midprofession [person] in a position to do just about something you ask with actually no questions.”
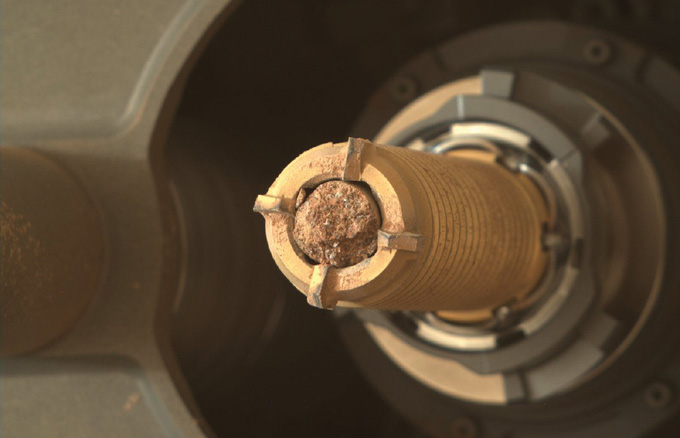
Perseverance is principally a duplicate of Curiosity constructed from its spare components, however with one main modification: a system for drilling, gathering and storing slender cores of rock. Perseverance’s job is to gather samples of Martian rock for future missions to deliver to Earth, in what could be the primary robotic pattern return from Mars. That will enable scientists to do subtle analyses of Martian rocks of their earthbound labs. “It feels, much more than earlier missions, that we’re doing this for the subsequent era,” Siebach says.
The rover is working quick. In contrast with Curiosity’s leisurely exploration of Gale crater, Perseverance has been zooming round its touchdown web site, the 45-kilometer-wide Jezero crater, since its February 2021 arrival. It has collected 10 rock cores and is already eyeing the place to place them down on the floor for future missions to select up. “We’re going to deliver samples again from a variety of areas,” says mission undertaking scientist Kenneth Farley of Caltech. “And so we maintain to a schedule.”
Perseverance went to Jezero to check an historical river delta, which incorporates layers of sediment that will harbor proof of historical Martian life. However the rover barely missed its goal, touchdown on the opposite facet of a set of impassable sand dunes. So it spent most of its first yr exploring the crater flooring, which turned out to be product of igneous rocks (SN: 9/11/21, p. 32). The rocks had cooled from molten magma and weren’t the sedimentary rocks that many had anticipated.
Scientists again on Earth will be capable to exactly date the age of the igneous rocks, primarily based on the radioactive decay of chemical components inside them, offering the primary direct proof for the age of rocks from a specific place on Mars.
JPL-CALTECH/NASA, ARIZONA STATE UNIV.
As soon as it completed exploring the crater flooring in March, the rover drove shortly towards the delta. Every successive NASA rover has had higher expertise in autonomous driving, in a position to determine hazards, steer round them and maintain going without having fixed directions from mission management.
Perseverance has a separate pc processor to run calculations for autonomous navigation, permitting it to maneuver sooner than Curiosity. (It took Curiosity two and a half years to journey 10 kilometers; Perseverance traveled that far in somewhat over a yr.) “The rover drives just about each minute that we may give it,” Farley says.
In April, Perseverance set a Martian driving report, touring almost 5 kilometers in simply 30 Martian days. If all goes effectively, it is going to make some journeys up and down the delta, then journey to Jezero crater’s rim and out onto the traditional plains past.
Perseverance has a sidekick, Ingenuity, the primary helicopter to go to one other world. The nimble flier, solely half a meter tall, succeeded past its designers’ wildest goals. The helicopter made 29 flights in its first 16 months when it was solely presupposed to make 5 in a single month. It has scouted paths forward and scientific targets for the rover (SN On-line: 4/19/22). Future rovers are nearly sure to hold somewhat buddy like this.
China’s debut
Whereas america has led in Mars rover exploration, it’s not the one participant on the scene. In Might 2021, China grew to become the second nation to efficiently place a rover on Mars. Its Zhurong rover, named after a mythological fireplace god, has been exploring half of a giant basin within the planet’s northern hemisphere often known as Utopia Planitia.
The touchdown web site lies close to a geologic boundary which may be an historical Martian shoreline. In contrast with the opposite Mars rover areas, Zhurong’s touchdown web site is billions of years youthful, “so we’re investigating a special world on Mars,” says Lu Pan, a planetary scientist on the College of Copenhagen who has collaborated with Zhurong scientists.
In some ways, Zhurong resembles Spirit and Alternative, in dimension in addition to mobility. It carries cameras, a laser spectrometer for finding out rocks and ground-penetrating radar to probe underground soil constructions (SN On-line: 5/19/21).
After touchdown, Zhurong snapped footage of its rock-strewn environment and headed south to discover a wide range of geologic terrains, together with mysterious cones that might be mud volcanoes and ridges that appear to be windblown dunes. The rover’s preliminary findings embody that the Martian soil at Utopia Planitia is much like some desert sands on Earth and that water had been current there maybe as lately as 700 million years in the past.
In Might, mission controllers switched Zhurong into dormant mode for the Martian winter and hope it wakes up on the finish of the season, in December. It has already traveled almost two kilometers throughout the floor, farther than the meager 100 meters that Sojourner managed. (To be honest, Sojourner needed to maintain circling its lander as a result of it relied on that lander to speak with Earth.)
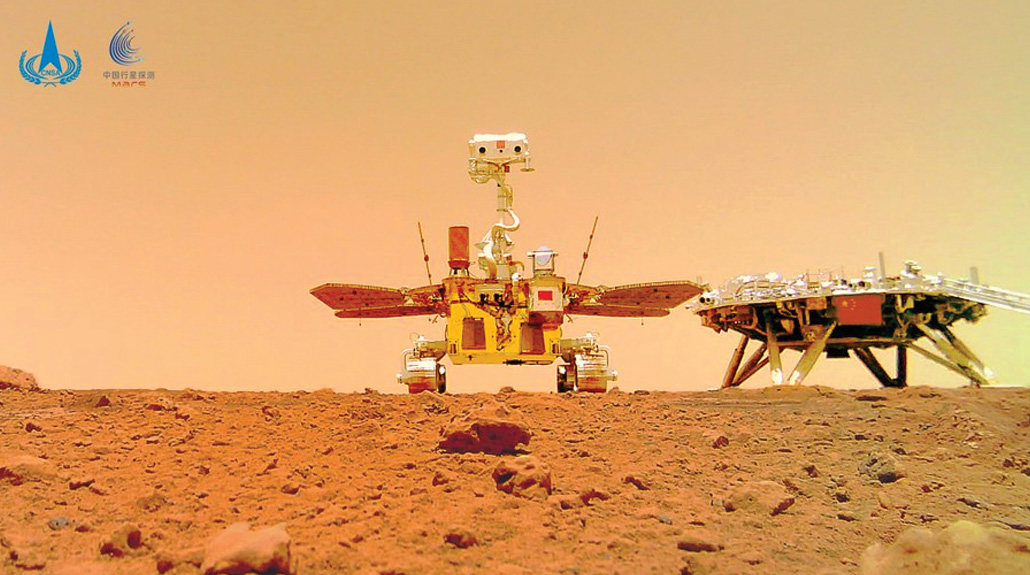
From Sojourner to Zhurong, the Mars rovers present what humankind can accomplish on one other planet. Future rovers would possibly embody the European House Company’s ExoMars, though its 2022 launch was postponed after Russia attacked Ukraine (SN: 3/26/22, p. 6). Europe terminated all analysis collaborations with Russia after the invasion, together with launching ExoMars on a Russian rocket.
Vasavada remembers his sense of awe on the Curiosity launch in 2011: “Standing there in Florida, watching this rocket blasting off and feeling it in your chest and understanding that there’s this extremely fragile complicated machine hurtling on the tip of this rocket.… It simply gave me this full impression that right here we’re, people, blasting this stuff off into house,” he says. “We’re little tiny human beings sending this stuff to a different planet.”



